VMware 服务器虚拟化环境搭建手册
文档目的
本文档旨在为系统管理员或 IT 工程师提供一份详尽的指南,用于在企业环境中规划和部署基于 VMware vSphere 的服务器虚拟化平台,通过遵循本手册的步骤,您将能够成功构建一个稳定、高效、可扩展的虚拟化基础架构。

目标读者
- 系统管理员
- IT 架构师
- 负责数据中心基础设施的 IT 专业人员
第一章:规划与准备
在开始安装之前,充分的规划和准备是成功的关键,这一步将决定您虚拟化环境的性能、可用性和可扩展性。
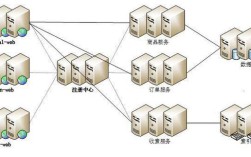
1 架构组件理解
一个标准的 vSphere 环境主要由以下组件构成:
- ESXi (ESXi Hypervisor):运行在物理服务器上的虚拟化层,直接安装在服务器的硬件上,用于创建和运行虚拟机,它是整个架构的基础。
- vCenter Server:中央管理平台,用于管理数据中心中所有的 ESXi 主机及其上的虚拟机,它提供统一的界面、集中配置、资源监控和高可用性功能。
- vSphere Client (HTML5):基于 Web 的用户界面,用于连接 vCenter Server 或直接连接 ESXi 主机,进行日常管理和操作。
- 虚拟机:在 ESXi 主机上运行的操作系统和应用程序。
- 数据存储:存放虚拟机文件(如.vmdk, .vmx, .nvram等)的存储设备,可以是本地磁盘、iSCSI、NFS 或 FC SAN。
- 虚拟网络:由 ESXi 主机上的虚拟交换机构成,用于连接虚拟机、物理网络以及 vMotion 等流量。
2 硬件选型
| 组件 | 推荐规格 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ESXi 主机 | - CPU: 2颗或以上 Intel Xeon / AMD EPYC 处理器,支持 Intel VT-x / AMD-V 硬件虚拟化。 - 内存: 256GB 或以上,支持 ECC 内存。 - 硬盘: 2块或以上 1.92TB+ U.2/NVMe SSD,用于安装 ESXi 系统;大量高性能 SSD/HDD 用于数据存储。 - 网卡: 4块或以上万兆 (10GbE) 网卡,用于管理、虚拟机、存储、vMotion 等不同流量隔离。 |
CPU 需要支持 Second Level Address Translation (SLAT),这对性能至关重要。 |
| 存储 | - 类型: 推荐使用全闪存阵列或超融合架构。 - 协议: NFS (简单易用) 或 iSCSI (成本效益高) 或 FC SAN (高性能)。 - 容量: 根据业务需求规划,考虑虚拟机增长和快照空间。 |
存储性能是虚拟化环境的瓶颈,务必保证 IOPS 和带宽。 |
| vCenter Server | - 物理机/虚拟机: 可部署在物理机或高可用的虚拟机集群中。 - CPU: 4核或以上。 - 内存: 16GB 或以上 (管理主机多时需增加)。 - 硬盘: 200GB+ SSD,用于存放数据库和系统文件。 |
生产环境强烈推荐部署在 vSphere HA 集群中,并配置外部数据库(如 PostgreSQL/SQL Server)。 |
3 网络规划
清晰的网络规划是保证虚拟化环境稳定运行的基础,建议使用 VLAN 进行隔离。
| 流量类型 | 建议VLAN | 用途 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 管理流量 | VLAN 10 | 用于 ESXi 主机的管理、IPMI/iDRAC、vCenter Server 访问。 | 每台主机至少1个IP。 |
| 虚拟机流量 | VLAN 20, 30, ... | 用于虚拟机访问生产网络。 | 可以创建多个,对应不同的业务网段。 |
| vMotion 流量 | VLAN 40 | 用于虚拟机在主机间的实时迁移。 | 必须独立且低延迟,建议万兆以上网络。 |
| 存储流量 (iSCSI) | VLAN 50 | 用于 iSCSI 存储网络的访问。 | 必须独立,避免与业务网络争抢带宽。 |
| vSphere Replication (VR) | VLAN 60 | 用于虚拟机复制,实现站点级容灾。 | 可选,根据容灾方案规划。 |
| vCenter Server / HA 流量 | VLAN 10 (与管理流量共用或独立) | vCenter Server 之间、vCenter 与 ESXi 主机之间的通信。 | 可与管理流量共用,但独立更佳。 |
4 IP 地址规划
| 主机/组件 | 用途 | 示例IP |
|---|---|---|
| ESXi Host 1 | 管理网络 | 168.10.11/24 |
| ESXi Host 2 | 管理网络 | 168.10.12/24 |
| vCenter Server | 管理网络 | 168.10.100/24 |
| 存储/NFS服务器 | 存储网络 | 168.50.10/24 |
第二章:安装与部署
本章将分步介绍 ESXi 和 vCenter Server 的安装过程。

1 安装 ESXi 主机
-
准备工作:
- 从 VMware 官网下载对应版本的 ESXi 安装镜像(
.iso文件)。 - 准备一台符合硬件要求的服务器,并连接好显示器、键盘、网络。
- 将 ESXi 镜像刻录到 U 盘或使用虚拟控制台挂载 ISO。
- 从 VMware 官网下载对应版本的 ESXi 安装镜像(
-
安装步骤:
- 将服务器设置为从 U 盘启动,进入 ESXi 安装界面。
- 按
Enter开始安装。 - 阅读并接受最终用户许可协议。
- 选择要安装的磁盘(通常是系统盘)。
- 设置 根密码(务必牢记,这是后续管理的关键)。
- 开始安装,等待进度条完成。
- 安装完成后,系统会自动重启,拔出 U 盘,进入 BIOS/UEFI 设置,将启动顺序改回从硬盘启动。
- 系统启动后,通过屏幕提示获取 ESXi 主机的 管理 IP 地址。
-
初始配置:
- 使用 Web 浏览器访问
https://<ESXi_IP地址>,https://192.168.10.11。 - 点击 "Download and Install" 或 "Launch ESXi Shell" 来安装 vSphere Client 插件,或直接使用 Web Client 进行管理。
- 在 "Host Configuration" -> "Network" 中,根据规划创建标准交换机,并将物理网卡分配给不同的端口组(如
Management,VM Network,vMotion)。
- 使用 Web 浏览器访问
2 安装 vCenter Server
注意: 生产环境推荐使用 vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA),它基于 Linux,部署和运维更简单,且内置了 PostgreSQL 数据库。
本节以 VCSA 8.x 为例:
-
准备工作:
- 从 VMware 官网下载 VCSA 的
.ova或.iso文件。 - 准备一台满足硬件要求的虚拟机或物理机。
- 确保目标网络可以访问 ESXi 主机、存储和 DNS 服务器。
- 从 VMware 官网下载 VCSA 的
-
部署步骤 (使用 OVA 文件):
- 在 vSphere Client 中,选择 "Deploy OVF Template"。
- 选择下载好的 VCSA
.ova文件。 - 部署选项: 选择 "部署为虚拟机"。
- 名称和位置: 输入 VCSA 的名称,并将其放置在您规划的集群和数据存储中。
- 部署配置: 选择 "大型" (Large) 或 "巨型" (Extra Large),根据要管理的 ESXi 主机数量和 vCenter 实例数量决定。
- 存储: 选择高性能的数据存储。
- 网络: 选择之前规划好的用于 vCenter 管理的端口组。
- 设置:
- Sizing: 根据提示设置 CPU、内存和磁盘大小。
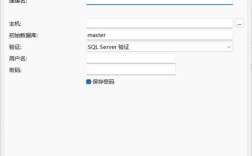
- Network: 设置 vCenter 的静态 IP 地址、子网掩码、网关和 DNS。
- Password: 设置 vCenter 的管理员密码(root 和 administrator@vsphere.local)。