- 本地解析:仅为当前 Linux 系统配置 DNS,用于解析域名。
- 客户端配置:配置 Ubuntu 客户端,让它使用指定的 DNS 服务器(例如公共 DNS 或内网 DNS)。
- 搭建 DNS 服务器:将 Ubuntu 机器配置成一个能为网络内其他设备提供域名解析服务的 DNS 服务器。
下面我将详细讲解这三种情况的配置方法。

本地解析(仅影响当前系统)
如果您只想让当前这台 Ubuntu 机器能够解析特定的域名(在本地开发环境中将 dev.example.com 指向 0.0.1),可以修改 /etc/hosts 文件。
编辑 hosts 文件
使用您喜欢的文本编辑器,nano 或 vim:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
添加或修改记录
文件格式为 IP地址 主机名,将 my-local-server 解析到 0.0.1:
0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 ubuntu-server
127.0.0.1 my-local-server
192.168.1.100 fileserver.example.com
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters保存并生效
保存文件后,更改会立即生效,可以使用 ping 命令测试:
ping my-local-server
配置客户端 DNS(使用指定的 DNS 服务器)
如果您想让这台 Ubuntu 机器使用公共 DNS(如 Google 8.8.8 或 Cloudflare 1.1.1)或您内网的 DNS 服务器,可以修改网络配置。
在 Ubuntu 18.04 及更高版本中,推荐使用 netplan 或 NetworkManager 来管理网络。
方法 A: 使用 Netplan (适用于服务器版和桌面版)
找到并编辑 Netplan 配置文件
配置文件通常位于 /etc/netplan/ 目录下,01-netcfg.yaml 或 50-cloud-init.yaml。
sudo nano /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
修改配置文件
在 nameservers 部分添加您希望的 DNS 服务器,可以添加多个。
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
# 将 eno1 替换为您的网卡名称,可以使用 ip a 命令查看
eno1:
dhcp4: yes
# --- DNS 配置开始 ---
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 1.1.1.1] # 使用 Google 和 Cloudflare 的 DNS
# 或者使用内网 DNS
# addresses: [192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2]
search: [example.com, mydomain.local] # 可选:添加域名搜索域
# --- DNS 配置结束 ---
应用配置
保存文件后,运行以下命令使配置生效:
sudo netplan apply
验证
检查 /etc/resolv.conf 文件是否已更新,并测试 DNS 解析:
cat /etc/resolv.conf # 应该能看到 nameserver 8.8.8.8 等内容 nslookup google.com
方法 B: 使用 NetworkManager (适用于桌面版 Ubuntu)
如果您使用的是 Ubuntu Desktop,图形界面是最简单的方式。
通过图形界面设置
- 点击右上角的网络图标。
- 选择“有线设置”或“Wi-Fi 设置”。
- 点击齿轮 ⚙️ 图标进入网络详情。
- 切换到“IPv4”或“IPv6”选项卡。
- 在“DNS”字段中,输入您希望的 DNS 服务器地址,用逗号分隔(
8.8.8, 1.1.1.1)。 - 点击“应用”保存。
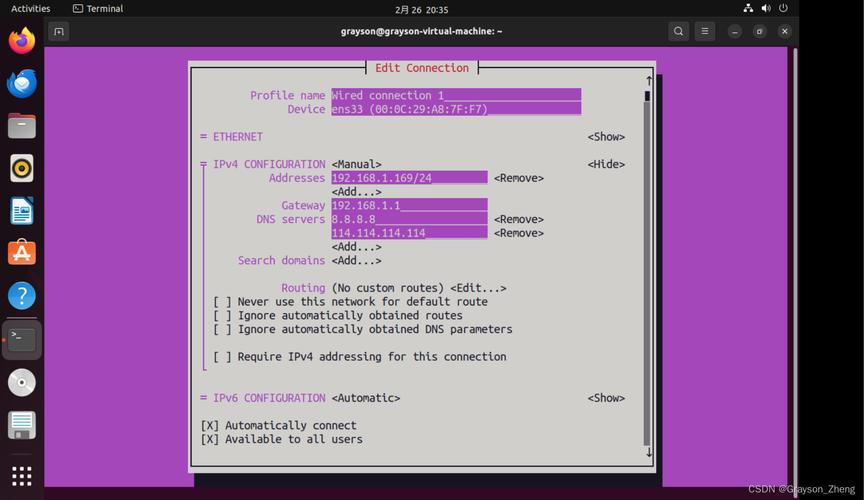
通过 nmcli 命令行工具
# 查看当前连接名称 nmcli connection show # 假设连接名为 "Wired connection 1",设置 DNS sudo nmcli connection modify "Wired connection 1" ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8,1.1.1.1" # 重新启动连接以应用更改 sudo nmcli connection down "Wired connection 1" && sudo nmcli connection up "Wired connection 1"
搭建 DNS 服务器(BIND9)
这是最复杂但功能最强大的方案,我们将使用最流行的 DNS 软件 BIND9 来配置一个权威 DNS 服务器或缓存 DNS 服务器。
安装 BIND9
sudo apt update sudo apt install bind9
主要配置文件
/etc/bind/named.conf: 主配置文件,通常只包含include指令。/etc/bind/named.conf.options: 全局选项,如监听地址、允许查询的地址等。/etc/bind/named.conf.local: 定义您自己的区域(Zone)。/var/cache/bind/: 存放区域数据文件和缓存文件。/etc/bind/db.*: 区域数据文件的模板。
基本配置示例
假设我们要为 example.com 这个域名创建一个权威 DNS 服务器。
步骤 1: 编辑主配置文件
sudo nano /etc/bind/named.conf.options
在 options 块中,设置只允许来自本地网络 (168.1.0/24) 的查询,并配置转发器(将无法解析的请求转发到公共 DNS)。
options {
directory "/var/cache/bind";
// 只允许来自 192.168.1.0/24 网络的查询
// allow-query { 127.0.0.1; 192.168.1.0/24; };
// 允许任何机器进行递归查询(如果作为缓存服务器)
allow-recursion { 127.0.0.1; 192.168.1.0/24; };
// 转发无法解析的请求到公共 DNS
forwarders {
8.8.8.8;
1.1.1.1;
};
// 如果没有转发器,就自己进行迭代查询
// forwarders { none; };
dnssec-validation auto;
listen-on-v6 { any; };
};
步骤 2: 定义区域
编辑 /etc/bind/named.conf.local 文件,添加 example.com 的正向和反向区域。
sudo nano /etc/bind/named.conf.local
//
// Do any local configuration here
//
// Consider adding the 1918 zones here, if they are not used in your
// organization
// include "/etc/bind/zones.rfc1918";
// --- 正向区域 example.com ---
zone "example.com" {
type master;
file "/etc/bind/db.example.com"; // 区域数据文件路径
};
// --- 反向区域 1.168.192.in-addr.arpa (假设你的网段是 192.168.1.x) ---
zone "1.168.192.in-addr.arpa" {
type master;
file "/etc/bind/db.192.168.1"; // 区域数据文件路径
};
步骤 3: 创建区域数据文件
我们需要创建两个文件:db.example.com 和 db.192.168.1。
创建正向区域文件 db.example.com
sudo cp /etc/bind/db.local /etc/bind/db.example.com sudo nano /etc/bind/db.example.com
如下:
;
; BIND data file for example.com
;
$TTL 604800
@ IN SOA ns1.example.com. admin.example.com. (
2 ; Serial
604800 ; Refresh
86400 ; Retry
2419200 ; Expire
604800 ) ; Negative Cache TTL
;
@ IN NS ns1.example.com.
@ IN A 192.168.1.100 ; 你的 DNS 服务器 IP
ns1 IN A 192.168.1.100 ; ns1 的 IP
www IN A 192.168.1.101 ; www 服务器的 IP创建反向区域文件 db.192.168.1
sudo cp /etc/bind/db.127 /etc/bind/db.192.168.1 sudo nano /etc/bind/db.192.168.1
如下:
;
; BIND reverse data file for 192.168.1.0/24
;
$TTL 604800
@ IN SOA ns1.example.com. admin.example.com. (
1 ; Serial
604800 ; Refresh
86400 ; Retry
2419200 ; Expire
604800 ) ; Negative Cache TTL
;
@ IN NS ns1.example.com.
100 IN PTR ns1.example.com. ; 192.168.1.100 的反向记录
101 IN PTR www.example.com. ; 192.168.1.101 的反向记录步骤 4: 设置权限并重启 BIND9
# 确保区域数据文件的所有者是 bind 用户 sudo chown bind:bind /etc/bind/db.example.com sudo chown bind:bind /etc/bind/db.192.168.1 # 检查配置文件语法 sudo named-checkconf sudo named-checkzone example.com /etc/bind/db.example.com sudo named-checkzone 1.168.192.in-addr.arpa /etc/bind/db.192.168.1 # 如果没有错误,重启 BIND9 服务 sudo systemctl restart bind9 sudo systemctl enable bind9
步骤 5: 验证
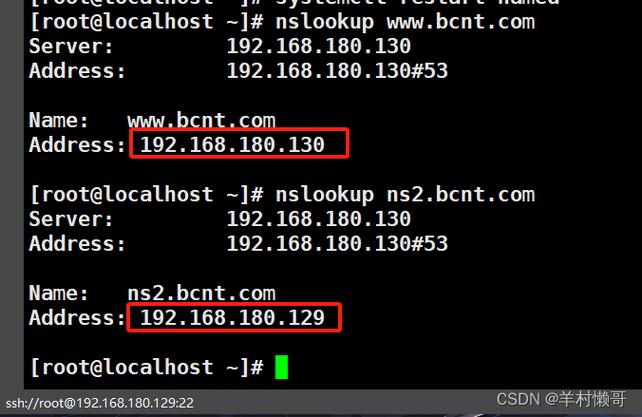
在您的 Ubuntu 服务器或其他客户端上,将 DNS 服务器指向 168.1.100,然后进行测试:
# 在客户端上设置临时 DNS sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf # 添加 nameserver 192.168.1.100 # 测试正向解析 nslookup www.example.com # 测试反向解析 nslookup 192.168.1.101
如果解析成功,说明您的 DNS 服务器已配置成功。
| 需求 | 工具/文件 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 本地解析 | /etc/hosts |
快速在本地添加域名到 IP 的映射,不影响其他设备。 |
| 客户端配置 | netplan, NetworkManager |
让当前机器使用更快的、更安全的或内网的 DNS 服务器。 |
| 搭建 DNS 服务器 | BIND9 (named) |
为整个局域网或互联网提供域名解析服务,功能强大且灵活。 |
根据您的具体目标选择合适的方案,对于大多数个人用户,方案二是最常用的,如果您需要管理一个网络,方案三则是必备技能。