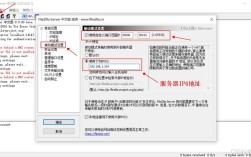
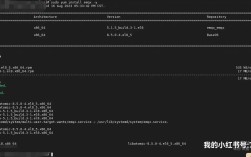
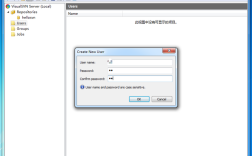
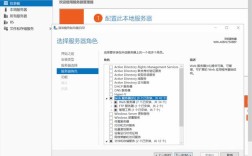
核心概念
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) 是一个简单的文件传输协议,通常用于网络设备的启动配置,如路由器、交换机、无线路由器等,它比 FTP 简单得多,但也没有认证和加密,功能非常有限,因此在生产环境中应谨慎使用。

第一步:安装 TFTP 服务器软件
你需要根据你的 Linux 发行版选择合适的软件包。
对于 Debian / Ubuntu 系统
我们使用 tftpd-hpa,这是一个非常流行且功能完善的 TFTP 服务器实现。
-
更新软件包列表
sudo apt update
-
安装 tftpd-hpa
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)sudo apt install tftpd-hpa
对于 CentOS / RHEL / Fedora 系统
我们使用 tftp-server,它通常是 xinetd 服务包的一部分。
-
安装 tftp-server 和 xinetd
# 对于 CentOS/RHEL 7/8 sudo yum install tftp-server xinetd # 对于 Fedora sudo dnf install tftp-server xinetd
第二步:配置 TFTP 服务器
安装完成后,你需要进行一些基本配置,主要是设置 TFTP 服务的根目录(客户端上传下载文件的默认位置)。
对于 Debian / Ubuntu (tftpd-hpa)
-
编辑配置文件 主配置文件是
/etc/default/tftpd-hpa,使用你喜欢的文本编辑器打开它,nano:sudo nano /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
-
修改配置项 你需要修改
TFTP_OPTIONS和TFTP_DIRECTORY这两项。# /etc/default/tftpd-hpa # 服务选项 # -l: 以独立模式运行,而不是通过 xinetd # -s: 指定 TFTP 根目录 TFTP_OPTIONS="--secure -l -s /srv/tftp" # TFTP 根目录 # 你可以自定义这个路径,/home/tftpboot TFTP_DIRECTORY="/srv/tftp" # 允许的客户端 # 默认是允许所有,你可以限制特定 IP # TFTP_ADDRESS=":69" # TFTP_EXTRA_OPTIONS="--create --permissive --address :69"
关键配置解释:
--secure: 这是一个非常重要的安全选项,它将 TFTP 服务限制在TFTP_DIRECTORY目录下,客户端不能通过 上级目录访问文件系统其他部分。-s /srv/tftp: 指定/srv/tftp为 TFTP 的根目录,如果这个目录不存在,你需要手动创建它。-l: 让tftpd-hpa作为独立服务运行,而不是依赖于xinetd,这是现代系统的推荐做法。
-
创建 TFTP 根目录并设置权限
# 创建目录 sudo mkdir -p /srv/tftp # 设置目录所有者为 tftp 用户(tftpd-hpa 安装时会自动创建) sudo chown -R tftp:tftp /srv/tftp # 设置目录权限为 755 (所有者可读写执行,组和其他用户可读执行) sudo chmod -R 755 /srv/tftp
对于 CentOS / RHEL / Fedora (tftp-server)
-
编辑配置文件 配置文件是
/etc/xinetd.d/tftp,使用nano或vim打开它:sudo nano /etc/xinetd.d/tftp
-
修改配置项 找到
server_args这一行,确保它指向了正确的根目录,disable选项被设置为no。# default: off # description: The tftp server serves files using the trivial file transfer \ # protocol. The tftp protocol is often used to boot diskless \ # workstations, to download configuration to network-aware printers, \ # and to transfer files between devices. service tftp { socket_type = dgram protocol = udp wait = yes user = root server = /usr/sbin/in.tftpd server_args = -s /var/lib/tftpboot -c disable = no per_source = 11 cps = 100 2 flags = IPv4 }关键配置解释:
server_args = -s /var/lib/tftpboot -c:-s /var/lib/tftpboot: 指定 TFTP 根目录为/var/lib/tftpboot,这是 CentOS/RHEL 的默认位置。-c: 允许客户端创建新文件,如果你只允许下载,可以去掉这个-c。
disable = no: 这行必须设置为no来启用 TFTP 服务。
-
创建 TFTP 根目录并设置权限
# 创建目录 (如果不存在) sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/tftpboot # 设置目录所有者为 root (tftp-server 通常以 root 身份运行) sudo chown -R root:root /var/lib/tftpboot # 设置目录权限为 755 sudo chmod -R 755 /var/lib/tftpboot
第三步:启动并启用服务
你需要启动 TFTP 服务并设置为开机自启。
对于 Debian / Ubuntu (使用 systemd)
# 启动 tftpd-hpa 服务 sudo systemctl start tftpd-hpa # 设置为开机自启 sudo systemctl enable tftpd-hpa # 检查服务状态 sudo systemctl status tftpd-hpa
对于 CentOS / RHEL / Fedora (使用 xinetd)
-
启用并启动 xinetd 服务
tftp-server是由xinetd超级服务器管理的,所以你需要启动xinetd。# 启动 xinetd 服务 sudo systemctl start xinetd # 设置为开机自启 sudo systemctl enable xinetd # 检查 xinetd 状态 sudo systemctl status xinetd
-
检查 tftp 服务状态 你可以检查
xinetd是否正在监听 TFTP 的 69 端口。# 查看 69 端口是否被监听 sudo netstat -ulnp | grep 69 # 或者使用 ss 命令 (更现代) sudo ss -ulnp | grep 69
如果看到类似
xinetd 0 0 0.0.0.0:69 0.0.0.0:*的输出,说明服务已经正常启动。
第四步:配置防火墙
TFTP 使用 UDP 协议的 69 端口,如果你的服务器开启了防火墙(如 ufw 或 firewalld),必须开放这个端口。
对于 Debian / Ubuntu (使用 UFW)
# 允许 TFTP (UDP 端口 69) 流量 sudo ufw allow tftp # 重新加载防火墙规则 (可选) sudo ufw reload
对于 CentOS / RHEL / Fedora (使用 Firewalld)
# 添加永久性的 TFTP 服务规则 sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=tftp # 重新加载防火墙规则以使新规则生效 sudo firewall-cmd --reload # 验证规则是否已添加 sudo firewall-cmd --list-services
第五步:测试 TFTP 服务器
这是验证一切是否正常工作的最后一步。
-
在服务器上放置一个测试文件
# 在 Debian/Ubuntu 上 echo "Hello from TFTP Server" | sudo tee /srv/tftp/test.txt # 在 CentOS/RHEL 上 echo "Hello from TFTP Server" | sudo tee /var/lib/tftpboot/test.txt
-
在客户端机器上测试下载 你可以在同一台服务器上测试,也可以在局域网内另一台 Linux 机器上测试,确保客户端安装了
tftp客户端工具。**安装 tftp