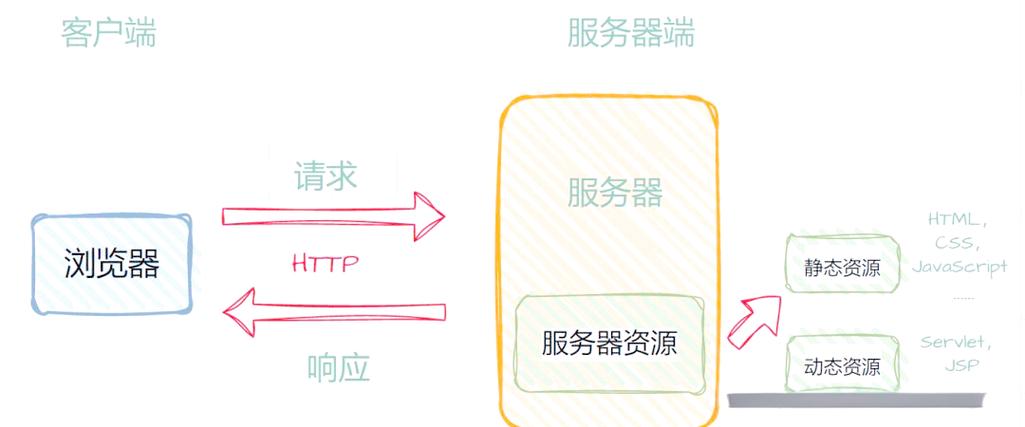
Java连接HTTP服务器是网络编程中的常见需求,广泛应用于数据交互、API调用、文件传输等场景,Java提供了多种方式实现HTTP连接,包括传统的HttpURLConnection、第三方库如Apache HttpClient和OkHttp,以及Java 11+引入的HttpClient,本文将详细介绍这些方法的核心原理、实现步骤及注意事项,帮助开发者根据实际需求选择合适的方案。
使用HttpURLConnection实现HTTP连接
HttpURLConnection是Java标准库中内置的HTTP客户端类,无需额外依赖,适合简单的HTTP请求场景,其核心步骤包括创建连接、设置请求参数、发送请求、处理响应等,以下以GET和POST请求为例说明实现方法。
GET请求示例
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class HttpGetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String urlString = "https://example.com/api/data";
URL url = new URL(urlString);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 设置请求方法
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
// 设置请求头(可选)
connection.setRequestProperty("User-Agent", "Java/1.8");
// 获取响应码
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("Response Code: " + responseCode);
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {
// 读取响应数据
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
System.out.println("Response: " + response.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("GET request failed");
}
connection.disconnect();
}
}
POST请求示例
POST请求需处理请求体数据,通常用于提交表单或JSON数据,以下以提交JSON数据为例:
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class HttpPostExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String urlString = "https://example.com/api/submit";
String jsonInputString = "{\"name\":\"John\", \"age\":30}";
URL url = new URL(urlString);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
connection.setDoOutput(true);
try (OutputStream os = connection.getOutputStream()) {
byte[] input = jsonInputString.getBytes("utf-8");
os.write(input, 0, input.length);
}
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("Response Code: " + responseCode);
connection.disconnect();
}
}
HttpURLConnection的优缺点
优点:
- 无需第三方依赖,Java标准库支持
- 适合简单的HTTP请求场景
- 支持基本HTTP方法(GET、POST、PUT等)和自定义请求头
缺点:
- 功能相对基础,缺乏高级特性(如连接池、异步请求)
- 处理复杂逻辑(如文件上传、多部分表单)代码较为繁琐
- 性能较低,不适合高并发场景
使用Apache HttpClient实现HTTP连接
Apache HttpClient是功能强大的开源HTTP客户端库,支持连接池、重试机制、异步请求等高级特性,适合企业级应用,需添加依赖(Maven):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.13</version>
</dependency>
基本GET请求示例
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
public class HttpClientGetExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try (CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault()) {
HttpGet request = new HttpGet("https://example.com/api/data");
request.addHeader("User-Agent", "Java/HttpClient");
try (CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request)) {
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
System.out.println("Response: " + result);
}
}
}
}
POST请求示例(JSON数据)
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
public class HttpClientPostExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try (CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault()) {
HttpPost post = new HttpPost("https://example.com/api/submit");
post.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
post.setEntity(new StringEntity("{\"name\":\"John\", \"age\":30}"));
try (CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(post)) {
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity());
System.out.println("Response: " + result);
}
}
}
}
HttpClient的核心优势
- 连接池管理:通过
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager复用连接,提升性能 - 重试机制:支持自动重试失败的请求
- 异步请求:通过
Future或回调实现非阻塞IO - 灵活的请求配置:支持自定义Cookie、认证、拦截器等
使用Java 11+ HttpClient实现HTTP连接
Java 11引入了标准化的HttpClient,取代了旧的HttpURLConnection,支持异步请求和WebSocket,是现代Java应用的首选。
同步GET请求示例
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
public class Java11HttpClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://example.com/api/data"))
.header("User-Agent", "Java/11")
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
System.out.println("Response: " + response.body());
}
}
异步POST请求示例
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class AsyncHttpClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://example.com/api/submit"))
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString("{\"name\":\"John\"}"))
.build();
CompletableFuture<HttpResponse<String>> future = client.sendAsync(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
future.thenAccept(response -> System.out.println("Response: " + response.body()));
// 等待异步请求完成
future.join();
}
}
Java 11 HttpClient的特性
- 简洁的API:链式调用设计,代码更易读
- 原生支持异步:通过
CompletableFuture实现非阻塞IO - 响应式编程支持:可与
FlowAPI结合 - WebSocket支持:内置WebSocket客户端实现
HTTP连接的常见问题及解决方案
| 问题场景 | 可能原因 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 连接超时 | 服务器响应慢或网络延迟 | 设置connection.setConnectTimeout(5000) |
| 中文乱码 | 响应编码未正确处理 | 明确指定编码:new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "UTF-8") |
| HTTPS证书错误 | 自签名证书或不受信任的CA | 禁用SSL验证(仅测试环境):connection.setSSLSocketFactory(TrustAllCertificates.createSSLFactory()) |
| 大文件上传内存溢出 | 直接读取整个文件到内存 | 使用分块上传或流式处理 |
相关问答FAQs
Q1: 如何处理HTTP请求中的HTTPS证书问题?
A: 对于自签名证书的HTTPS服务器,可以通过自定义SSL上下文禁用证书验证(仅建议测试环境使用):
TrustManager[] trustAllCerts = new TrustManager[] {
new X509TrustManager() {
public java.security.cert.X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() { return null; }
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType) {}
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] certs, String authType) {}
}
};
SSLContext sc = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL");
sc.init(null, trustAllCerts, new java.security.SecureRandom());
HttpsURLConnection.setDefaultSSLSocketFactory(sc.getSocketFactory());
Q2: 如何实现HTTP连接的自动重试机制?
A: 可以结合RetryPolicy实现自定义重试逻辑,以下是Apache HttpClient的重试示例:
HttpRequestRetryHandler retryHandler = (exception, executionCount, context) -> {
if (executionCount >= 3) {
return false; // 超过最大重试次数
}
if (exception instanceof NoHttpResponseException) {
return true; // 服务器无响应时重试
}
return false;
};
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setRetryHandler(retryHandler)
.build();