第一步:最简单的检查(快速排除法)
-
重启大法:这是最简单也最有效的方法。
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 重启你的电脑。
- 重启你的路由器和光猫:将路由器和光猫的电源拔掉,等待1-2分钟,然后先插上光猫电源,等它所有指示灯稳定(通常需要1-2分钟),再插上路由器电源,等它指示灯稳定,这个操作可以解决大部分临时的软件或缓存问题。
-
检查其他设备:
- 用你的手机连接同一个Wi-Fi,看能否上网。
- 如果手机能上网,说明问题出在你的电脑上。
- 如果手机也不能上网,说明问题出在路由器、光猫或外线上,请直接跳到 第四步。
第二步:如果问题出在你的电脑上(其他设备正常)
请按顺序执行以下操作:
检查网络配置(IP地址问题)
有时候电脑获取的IP地址有问题,导致无法正确上网。
-
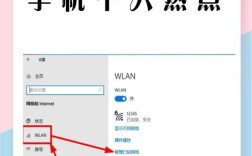
对于Wi-Fi用户:
 (图片来源网络,侵删)
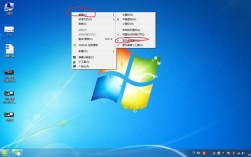
(图片来源网络,侵删)- 右键点击右下角的网络图标,选择“网络和 Internet 设置”。
- 点击“更改适配器选项”。
- 找到你的Wi-Fi连接(通常叫“WLAN”),右键点击它,选择“禁用”。
- 等待几秒钟,再次右键点击它,选择“启用”。
- 系统会自动重新获取IP地址,然后尝试上网。
-
对于网线用户(有线连接):
- 同样在“更改适配器选项”中,找到你的“以太网”连接。
- 右键点击,选择“禁用”,然后再次“启用”。
运行Windows网络诊断工具
Windows系统内置了诊断工具,可以自动检测并修复一些常见问题。
- 右键点击右下角的网络图标。
- 选择“网络和 Internet 设置”。
- 在左侧菜单中点击“状态”。
- 向下滚动,找到“网络重置”,点击它,然后选择“立即重置”。
- 注意:此操作会删除你所有的网络适配器,并将它们还原到出厂设置,重置后电脑会自动重启,你需要重新连接Wi-Fi或设置有线网络,这是一个大招,通常很有效。
刷新DNS缓存
DNS(域名系统)负责将网址(如 www.google.com)翻译成IP地址,DNS缓存出错会导致无法解析网址。
- 在开始菜单搜索“cmd”或“命令提示符”。
- 右键点击“命令提示符”,选择“以管理员身份运行”。
- 在黑色的窗口中,依次输入以下命令,每输完一行按一次回车:
ipconfig /flushdns netsh winsock reset - 命令执行完成后,重启电脑,然后再次尝试上网。
检查防火墙和安全软件
防火墙或第三方杀毒软件会错误地拦截网络连接。

- 暂时关闭Windows Defender防火墙:
- 进入“设置” > “隐私和安全性” > “Windows 安全中心”。
- 点击“防火墙和网络保护”。
- 分别点击“域网络”、“专用网络”、“公用网络”,将每个网络的防火墙“关闭”。
- 尝试上网,如果可以了,说明是防火墙规则问题,可以尝试开启并调整规则,或者暂时保持关闭并安装其他安全软件。
- 暂时禁用第三方杀毒软件:如果你安装了360、火绒、腾讯电脑管家等,尝试右键点击其图标,选择“退出”或“暂时禁用”,然后测试网络。
第三步:如果问题出在所有设备上(路由器或外网问题)
如果连手机也连不上网,那问题出在路由器或更外部的设备上。
检查物理连接(网线和指示灯)
- 检查光猫和路由器的指示灯:
- 光猫:看“PON”(或“注册”)灯是否常亮或绿色,如果闪烁或不亮,说明外线问题,需要联系你的网络运营商(如电信、联通、移动)。
- 路由器:看“WAN”口(通常是蓝色或与其他口颜色不同)的灯是否闪烁,如果灯不亮,说明路由器和光猫之间的网线可能没插好或损坏。
- 重新插拔所有网线:将连接光猫和路由器的网线,以及连接路由器和电脑的网线,都拔下来再重新插紧,确保两端都插牢固。
登录路由器管理后台
- 确保你的电脑连接到了路由器的Wi-Fi(通过网线连接到路由器LAN口也可以)。
- 打开浏览器,在地址栏输入路由器的管理地址,通常是
168.1.1、168.0.1或tplogin.cn(具体看路由器底部标签)。 - 输入用户名和密码登录。
- 检查以下几个关键设置:
- WAN口设置:查看是否是“动态IP”(DHCP)上网方式,如果不是,尝试改为“动态IP”并保存重启。
- 拨号设置:如果你家是宽带拨号,检查PPPoE的用户名和密码是否正确。
- DHCP服务器:确保DHCP服务是“启用”状态,这样电脑才能自动获取IP地址。
- 固件(Firmware):检查是否有新的固件可以更新,新固件可能修复了旧版本的Bug。
重置路由器
如果登录后台后设置混乱,或者不确定如何修改,可以直接重置路由器。
- 找到路由器上的“Reset”小孔,用牙签或卡针长按10-15秒,直到所有指示灯闪烁。
- 重置后,路由器会恢复到出厂设置,你需要重新设置Wi-Fi名称、密码,并选择上网方式(通常是“动态IP”或“PPPoE拨号”)。
第四步:寻求专业帮助
如果你尝试了以上所有方法,问题仍然存在,那么很可能是硬件问题或运营商的外部线路问题。
- 联系你的网络运营商:打电话给电信、联通或移动的客服,报修宽带故障,他们可以远程检测你的线路状态,并安排维修人员上门检查。
- 硬件故障:可能是光猫或路由器本身损坏了,可以尝试用一个已知正常的路由器替换你现在的路由器进行测试,来判断是路由器坏了还是其他问题。
总结一下排查思路
电脑有网但上不了网 = 本地通,但出不去
- 先重启,最简单。
- 看其他设备,判断问题范围(电脑问题 vs 全局问题)。
- 电脑问题:禁用/启用网络 -> 网络重置/刷新DNS -> 检查防火墙。
- 全局问题:检查指示灯和网线 -> 登录路由器后台检查/重置路由器 -> 联系运营商。
希望这个详细的指南能帮助你解决问题!